A crankshaft and Camshaft position sensor indicate the position of the valves and the pistons in an internal combustion engine. The position of a valve or a piston is important to maintain the firing order of the engine. In this article, I will discuss the benefits and usefulness of Crankshaft and Camshaft position sensors.
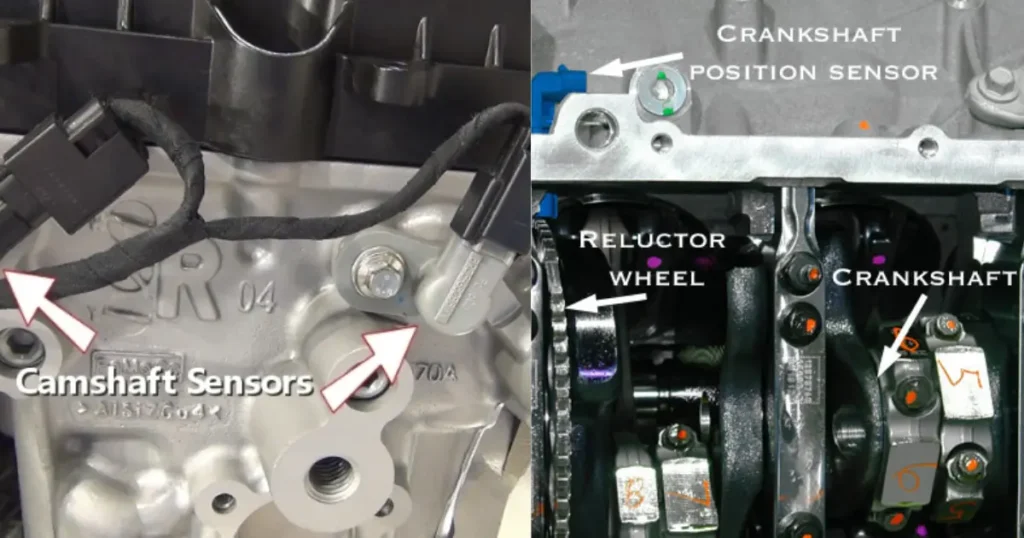
Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor
The modern marvels under the hood of our vehicles are a result of intricate systems working seamlessly together. Two vital components contributing to this symphony are the crankshaft position sensor and the camshaft position sensor.
The crankshaft position sensor is a small yet powerful device that monitors the rotation of the crankshaft, a critical engine component. It sends signals to the engine control module, providing real-time data on the crankshaft’s position.
Complementing the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft position sensor monitors the rotation of the camshaft. Together, these sensors ensure precise coordination, crucial for maintaining accurate engine timing. The valve opening by the actuators is determined by this system.
So, operating together of these two valves together is important for engine operation. The function and the benefits of these valves are important for fuel injection and emission control systems.
Read More- Gas Turbine Cycles | Open Cycle and Closed Cycle Gas Turbine.
Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor Working Principle

These sensors play crucial roles in providing information about the positions of the crankshaft and camshaft to the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Engine Control Unit (ECU).
The CKP(Crankshaft Position Sensor) sensor monitors the rotational position of the crankshaft. It detects the crankshaft’s speed and position, sending this information to the ECM. Typically mounted near the crankshaft, often at the front or rear of the engine. This sensor helps the ECM determine the precise timing for fuel injection and ignition. It’s critical to synchronize these processes with the engine’s rotation.
The CMP(Camshaft Position Sensor) sensor monitors the rotational position of the camshaft. It provides information about the camshaft’s position and speed to the ECM. This sensor is positioned near the camshaft, usually on the cylinder head. The sensor assists the ECM in accurately timing the opening and closing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves. This timing is crucial for overall engine performance and efficiency.
Both sensors contribute to the precise timing of fuel injection and ignition, optimizing engine efficiency and performance. The ECM uses data from these sensors to ensure that the engine’s valves open and close at the right time and that the fuel injection and ignition timing are synchronized with the engine’s rotation.
Read More- What is the Importance of Maintenance of Automobiles?
Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
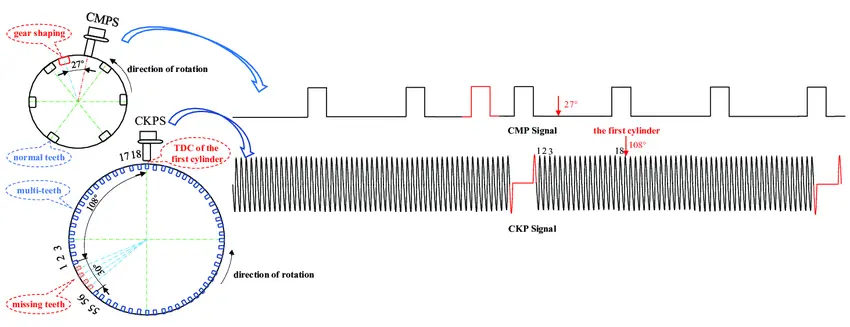
The sensor is a magnetic or Hall effect sensor that generates electrical signals based on the crankshaft’s rotation. The sensor is connected to the ECM through a wiring harness. The wiring carries the electrical signals from the CKP sensor to the ECM.
The ECM processes the signals received from the CKP sensor to determine the crankshaft’s position and speed. The CKP sensor requires a power supply and a ground connection to function properly. The ECM ensures the sensor receives the necessary power.
Similar to the CKP sensor, the CMP sensor generates electrical signals based on the camshaft’s rotation. The CMP sensor is connected to the ECM through a wiring harness. The wiring carries the electrical signals from the CMP sensor to the ECM.
The ECM processes the signals received from the CMP sensor to determine the camshaft’s position and speed. Similar to the CKP sensor, the CMP sensor requires a power supply and a ground connection to function correctly. The ECM ensures the sensor receives the necessary power.
The wiring harnesses for both the CKP and CMP sensors play a crucial role in transmitting the electrical signals accurately. Any damage or disruption in the wiring can lead to sensor malfunction.
Read More- Pollution from Motor Vehicles and Its Control.
Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor Function
Both the sensors have the different functions in the engine. The major function of this sensor is to give the location of the crankshaft and the camshaft to the ECU. The CKP sensor monitors the rotational position and speed of the crankshaft.
The CKP sensor’s data is used by the ECM to determine the precise timing for fuel injection and ignition events. It helps the ECM identify the position of each piston within the engine’s cycle, enabling accurate fuel delivery and ignition timing for each cylinder.
Also, the CMP sensor monitors the rotational position and speed of the camshaft. The CMP sensor’s data is crucial for determining the timing of the opening and closing of the engine’s intake and exhaust valves. It enables the ECM to synchronize the operation of the camshaft with the crankshaft, ensuring optimal engine performance.
Read More- What is an Air Brake System? Read the Working and Advantages.
Types of Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensors
Crankshaft Position Sensors (CKP) and Camshaft Position Sensors (CMP) come in different types, each utilizing various technologies for position detection.
The types of Crankshaft Position Sensors are-
1. Hall Effect Sensors
These sensors use a Hall effect transducer to detect changes in magnetic fields as the crankshaft rotates. The sensor produces a voltage signal that the ECM interprets to determine the crankshaft position.
2. Variable Reluctance Sensors
This type of sensor generates a voltage signal by measuring changes in magnetic reluctance as the crankshaft rotates. The varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the sensor, allowing the ECM to determine the crankshaft position.
3. Optical Sensors
Some crankshaft position sensors use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photodiodes to detect slots or notches on a rotating disc attached to the crankshaft. The interruptions in the light signal correspond to specific crankshaft positions.
The types of Camshaft Position Sensors are-
1. Magnetic Hall Effect Sensors
Similar to those used in crankshaft position sensors, these sensors detect changes in magnetic fields as the camshaft rotates. The resulting voltage signal informs the ECM about the camshaft’s position.
Read More- What is the Meaning of CC of an Engine?
2. Variable Reluctance Camshaft Sensors
These sensors operate on the principle of magnetic reluctance, generating a voltage signal based on changes in the magnetic field as the camshaft rotates.
3. Optical Camshaft Sensors
Similar to optical crankshaft sensors, these sensors use light-based technology to detect slots or windows on a rotating disc attached to the camshaft. The interruptions in the light signal provide information about the camshaft’s position.
4. Hybrid Sensors
Some modern sensors combine Hall effect and magnetoresistive technologies to enhance accuracy and reliability in detecting camshaft position.
Advantages of Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor
So the advantages of these types of sensors are-
- By providing real-time data on the positions and speeds of the crankshaft and camshaft, these sensors enable the Engine Control Module (ECM) to precisely control ignition timing, fuel injection timing, and valve timing.
- Accurate timing control allows the engine to burn the air-fuel mixture more efficiently, leading to better fuel economy.
- The precise control of combustion parameters enabled by crankshaft and camshaft position sensors contributes to reduced emissions.
- The sensors play a crucial role in detecting abnormal combustion, such as engine knock.
- In engines equipped with VVT systems, camshaft position sensors play a key role in adjusting valve timing.
Conclusion
In summary, crankshaft and camshaft position sensors are integral to modern engine management systems, offering precise control over critical engine parameters. Their advantages include improved performance, fuel efficiency, emissions control, and diagnostic capabilities, ultimately contributing to a more reliable and environmentally friendly operation of internal combustion engines.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’S)
How often should crankshaft and camshaft sensors be inspected?
Regular inspections are recommended, ideally during routine vehicle maintenance checks.
What causes engine misfires associated with sensor issues?
Engine misfires can result from inaccurate data provided by faulty sensors, affecting fuel injection and timing.
Can I replace these sensors myself?
While it’s possible, consulting a professional is advisable for accurate diagnosis and replacement.
Are there generic sensors compatible with multiple car models?
Some sensors may have universal compatibility, but it’s crucial to verify compatibility for specific vehicle models.
What advancements can we expect in sensor technology in the coming years?
Future sensor technology may focus on enhanced accuracy, faster data transmission, and integration with advanced engine control systems.


Do comment here