Last Updated on 22 July 2024 by automobilehut.in
Differential and its construction are discussed in this article. The differential is the housing where the movement of the two wheels differentiates when the vehicle takes a turn. The differential is an important component as it saves the vehicle from rolling over in any true condition. So read the article.
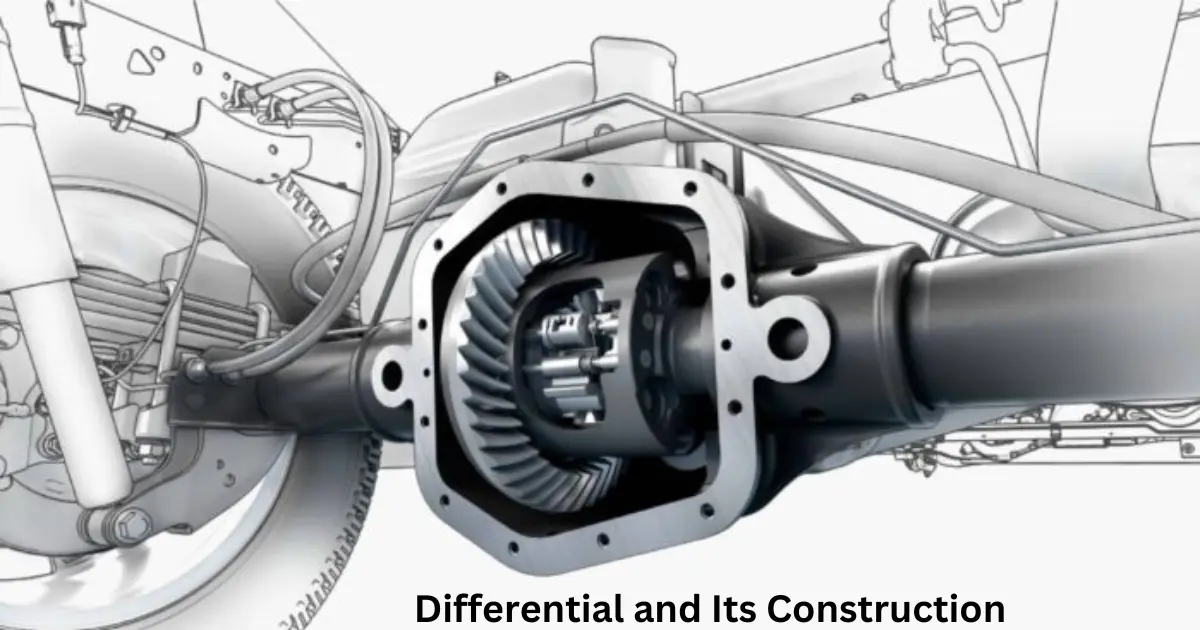
What is a Differential
If a car travels in a straight line, the two rear wheels turn on the road exactly at the same speed. There is no relative movement between the two rear wheels. The propeller shaft may be geared rigidly, in this case, with the rear axle to rotate the rear wheels together.
But when the car takes a turn, the outer wheel travels on a longer radius than the inner wheel. The outer wheel turns faster than the inner wheel, that is, there is a relative movement between the two rear wheels. If the two rear wheels are rigidly fixed to a rear axle, the inner wheel will slip, which will cause rapid tire wear, steering difficulties, and poor road holding.
Therefore, there must be some devices to provide relative movement to the two rear wheels when the car is taking a turn. The differential serves this purpose.
The differential is part of the inner axle housing assembly, which includes the differential, rear axles, wheels, and bearings. The differential consists of a system of gears arranged in such a way that they connect the propeller shaft with the rear axles.
The purpose of the differential is to provide relative movement to the two rear wheels when the car is taking a turn. The torque transmitted to each wheel is, however, always equal.
Read more- 6 Types of Suspension Systems Used in Cars in 2024
Differential and Its Construction
The sun gears are mounted on the inner end of each rear axle (called the half shaft). A differential cage is assembled on the left axle. A ring gear (called the crown gear) is attached to the case so that the cage rotates with the crown gear.
The crown gear is driven by the bevel pinion. Both the crown wheel and the cage are free on the left rear axle. The cage supports two planet pinions (called the differential pinion gears) on a shaft that meshes with the two sun gears. Thus, when the differential cage is rotated, both the sun gears rotate, and thus both wheels turn, which are attached to the outer end of the rear axles.
Usually, a housing encloses gears and bearings that make up the rear differential assembly. The transmission sends power to the rear differential, which uses different axles to distribute it to each wheel. The wheels can revolve at different speeds and yet receive torque from the engine thanks to the gears inside the differential.
For the most part, the rear differential structure is responsible for providing stable and smooth driving, particularly while navigating curves or rough terrain.
Read more- 10 Reasons Why Electric Cars are the Future of Automotive
Working of Differential

Now let us suppose that one wheel is held stationary. Then, when the differential cage is rotated, the planet gears will also rotate as they run around on the stationary axle sun gear.
While rotating in this manner, the planet pinions carry the rotary motion to the other axle sun gear, causing it, and the wheel too, to rotate. Therefore, one rear wheel turns more rapidly than the other, and while the car is taking a turn, the planet gears spin on its shaft, transmitting more rotary motion to one rear wheel than to the other.
When both wheels turn at the same speed, the planet pinions do not rotate on a shaft. Thus, when a car is running in a straight line, the crown wheel, differential cage, planet pinions, and sun gears all turn as a unit without any relative motion. But when the car takes a turn, the planet pinions rotate on their shaft to permit the outer rear wheel to turn more rapidly than the inner wheel.
However, during a turn, the outer wheel needs to cover a greater distance than the inner wheel. The differential allows for this by allowing the side gears to rotate at different speeds. The spider gears distribute the power to each wheel accordingly, enabling the vehicle to navigate the turn smoothly without skidding or loss of traction.
Read more- The Role of AI in Internal Combustion Engine Optimization
Advantages of Differential
The differential provides a lot of advantages for the vehicle. The advantages are:
- Differential helps to keep the traction on the roads as it provides equal rotating speeds.
- It helps to provide stability to the vehicle when taking a turn.
- The power is distributed equally to each of the wheels.
- Differential helps reduce the wear and tear on the tires.
- It helps prevent loss of traction and skidding, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing driver confidence behind the wheel.
Disadvantages of Differential
As for advantages, it has disadvantages as well. The disadvantages of this system are:
- The differential is a complex housing, as it has gears, bearings, and shafts. It also causes difficulties while servicing.
- Some vehicles are equipped with limited slip differentials, so the traction can not work effectively on the other roads.
- The differential can be heated, just because of the friction of the moving parts, and no other continuous lubrication systems are there.
- During turns, the vehicle loses power as one of the dedicated wheels does not need any additional power to move.
Conclusion
Overall, while differentials are essential for maintaining traction, stability, and drivability in vehicles, they also come with certain drawbacks that manufacturers and drivers need to consider. Balancing the advantages and disadvantages of differential design and implementation is crucial for optimizing vehicle performance and reliability.
