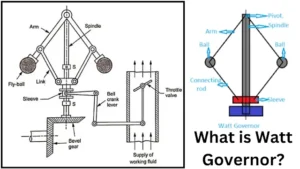
The automotive industry is now on a role in technology and manufacturing. In this article, I will discuss What is Watt Governor in Automobile engines.
 Technical Education
Technical Education
What are the Different Types of Resistance on Vehicles?
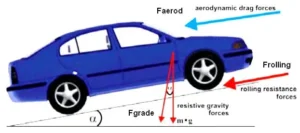
When a vehicle starts to move a lot of resistance comes to stop the vehicle. In this article, I will discuss the different types of resistance in vehicles.
Different Types of Resistance on Vehicles
- Rolling resistance.
- Wind or air resistance.
- Gradient resistance.
These are three types of resistance that pull back the vehicle. Each of these resistances is discussed below.
1. Rolling Resistance
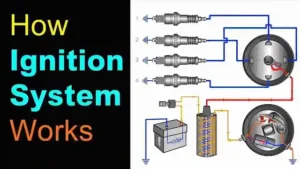
How Does a Distributor-Based Ignition System Work?
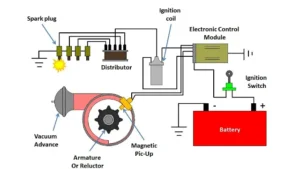
The distributor-based ignition system is a mechanical ignition system where the engine’s moving parts help to get the ignition done. In this article, I will discuss what a Distributor-Based Ignition System?
Distributor-Based Ignition System
How Does a Distributor Type Ignition System Work
Components of Distributor
What is Contact Breaker?
What is contact breaker is discussed in this article. The working principle and the types are also discussed. What is …
What is Detonation in an Engine?
Detonation in an engine means the rise of sudden pressure in an internal combustion engine, which affects the engine components. In this article, I will discuss the meaning of Detonation in an Engine, the factors affecting detonation, etc.
Detonation in an Engine
Process of Detonation in an Engine
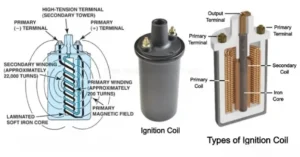
Different Types of Ignition Coils and Their Functions.
Types of Ignition Coils
The ignition coil has two types-
- Core Type Ignition Coil.
- Can Type Ignition Coil.
What is an Ignition Coil
Core Type Ignition Coil
Ignition System | Ignition System of the Spark Ignition Engine.
The ignition system of the spark ignition engine is conducted by the spark plug at the end of the compression stroke. In this article, I will discuss the Ignition System and its types with a diagram.
Ignition System
Requirements of an Ignition System
1. Spark Generation
2. Timing Control
3. Voltage Regulation
4. Durability and Heat Resistance
5. Compatibility with Fuel Types
Types of Ignition Systems
- Battery Ignition System.
- Magneto Ignition System.
Battery Ignition System
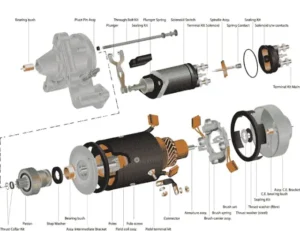
Starter Motor Maintenance | Tips for Repair.
Starter motor maintenance is important for starting the engine properly. In this article, I will discuss the starter motor maintenance …
Basic Starter Motor Problems in a Car.
Starter motor problems can prevent your vehicle from starting. The starter motor is responsible for starting the engine with a cranking.
Starter Motor Problems
- The starter motor does not turn to crank the engine.
- The starter motor cranks the engine slowly.
- The starter motor spins but does not crank the engine.
- The starter gear fails to disengage when the engine starts.
1. The Starter Motor does not Turn to Crank the engine
New Ola S1x Scooter launched in India automobilehut
The new Ola S1x scooter is launched in India with new features and stylish design. Read this article for better knowledge of this bike before buying it.
New Ola S1x Scooter
Power
Price
| Variant | Price | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| S1X 2KWH | 90,019 (Ex-showroom) | 91 km, 85 kmph |
| S1X 3KWH | 99,979 (Ex-showroom) | 151 km, 90 kmph |
| S1X plus | 1,09,827 (Ex-showroom) | 151 km, 90 kmph |