Automobile
Types of Hammer in Hindi | Hammer ke Prakar.
Types of Hammer in Hindi
Top 10 Best Car Service Company in India.
SBI General Insurance in Hindi | एसबीआई सामान्य बीमा
Function of an Exhaust System | Full Details.
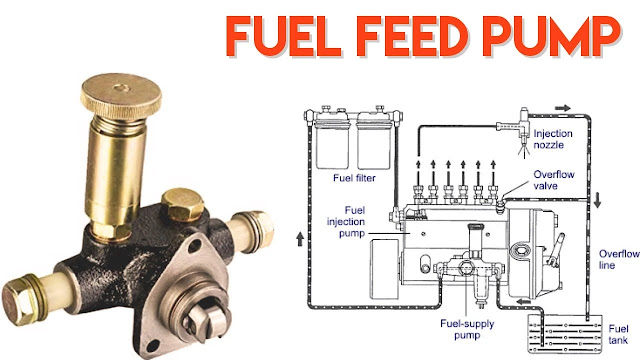
What is A Fuel Feed Pump for Diesel Engine?
Fuel Feed Pump–
Fuel Feed Pump comes in various types, including mechanical and electric pumps. Mechanical Fuel Feed Pump is typically used in older vehicles and is driven by the engine’s camshaft or a dedicated shaft. They rely on a diaphragm or plunger to draw fuel from the tank and push it toward the engine. On the other hand, electric fuel feed pumps are more common in modern vehicles and use an electric motor to draw fuel from the tank and transfer it to the engine.
Fuel feed pumps operate on the principle of positive displacement, which means that they deliver a consistent amount of fuel to the engine regardless of the engine’s demand. This is essential to ensure that the engine always receives the correct amount of fuel to run efficiently and avoid damage. Fuel Feed Pumps are also designed to maintain a specific fuel pressure, which is necessary to achieve the optimal fuel-air mixture for combustion.
In addition to transferring fuel to the engine, Fuel Feed Pumps also play a critical role in removing air and vapor from the fuel system. Air and vapor can form in the fuel tank and lines due to temperature changes or a low fuel level. These pockets of air can disrupt the fuel flow and cause the engine to run poorly or stall. Fuel feed pumps use a venting system to remove any air or vapor in the fuel system and maintain a consistent flow of fuel to the engine.
Fuel Feed Pump Design–
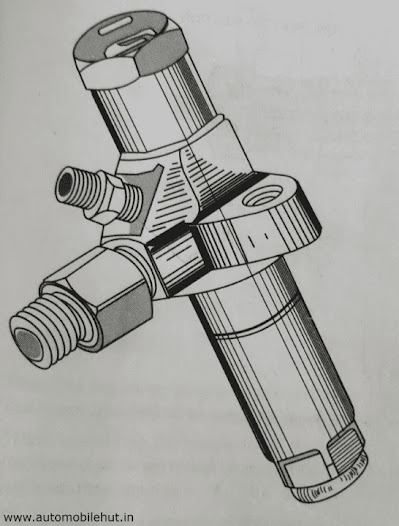
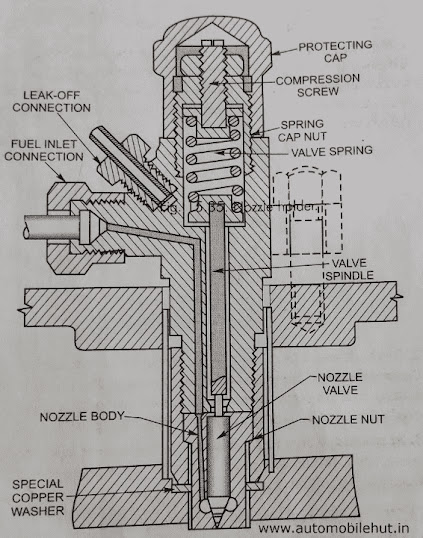
What is Fuel Nozzle Holder Assembly?
Nozzle holder–
Nozzle holder assembly–
The metal of the cylinder head, the faces of the copper joint washer, and the face of the nozzle cap nut should be cleaned in order to facilitate the making of a leak-proof joint. It is also advisable to fit a new joint washer whenever the Nozzle Holder is replaced after having been removed for cleaning.
When fitting the Nozzle Holder in position, care should be taken to see that it is an easy fit in the cylinder head tunnel and on the holding-down studs, so that it can be placed down on the copper joint without force of any kind. If the nozzle end seems tight in the injector pocket, the pocket should be tightened down evenly in order to prevent the nozzle from being canted and so “nipped ” in the cylinder head. This is very important, since any unevenness in tightening down may cause distortion of the nozzle and subsequent failure of the latter.
Fuel Injector Nozzle Types | Full Details.
A fuel injection nozzle is a component of an internal combustion engine that is responsible for delivering fuel into the engine’s combustion chamber. The nozzle is designed to atomize the fuel into a fine mist, which improves combustion efficiency and reduces emissions.
Fuel injector nozzle types–
1. Single-hole nozzle
2. Multi-hole nozzle
3. Long stem nozzles
4. Pintle nozzles
Fuel Injection Nozzle Function and operation.
Fuel injection nozzles are devices used in fuel injection systems to deliver fuel into an internal combustion engine. These nozzles …
Diesel Fuel Filters | All You Have to Know.
Diesel fuel filters–
Diesel fuel filters- method of operation-
Prior to putting it into operation or after cleaning and changing the filter element the filter must be filled with fuel oil through the filler plug orifice on the filter cover. After filling, the filler plug should be replaced immediately and the filtered air vented.