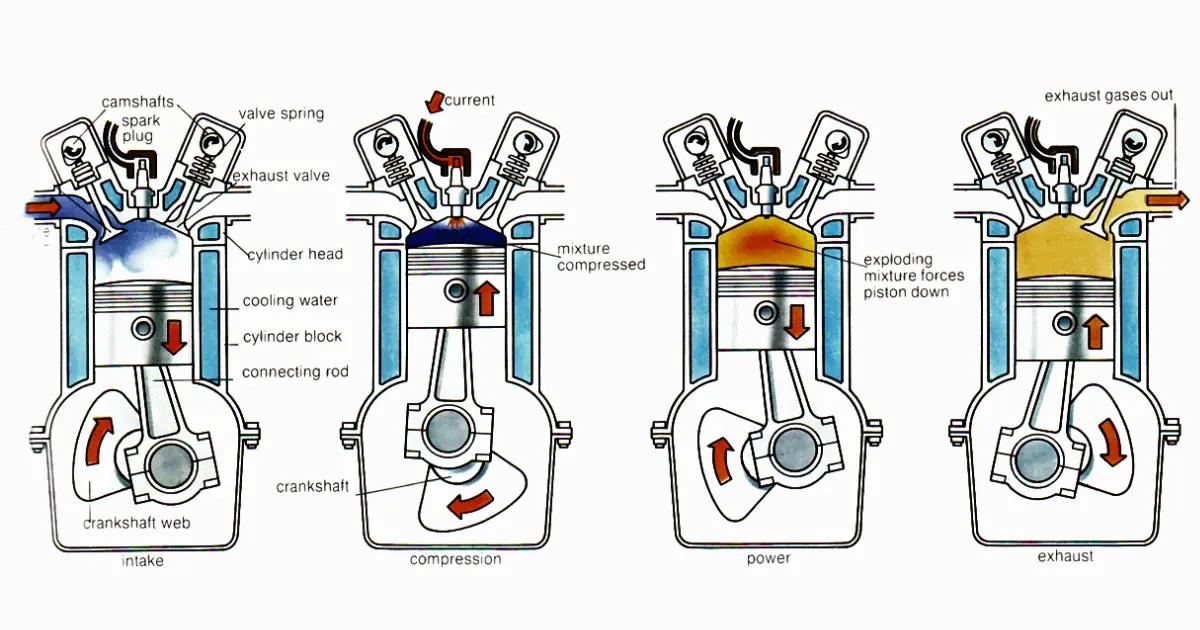
A four-stroke engine is the most used engine in an automobile vehicle. Engine is the most complicated device used in a vehicle. Before times were 2-stroke engine was used. In this article, I will discuss the details of the Four-Stroke Engine.
What is a Four-Stroke Engine
A four-stroke engine is an internal combustion engine where the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. This cycle was partially formed by the German scientist Otto in 1876, although it was described by French scientist Beande Roches in 1862. Every stroke is completed with 1800 turning of the crankshaft. The four strokes are- Suction, Compression, Power, and Exhaust.
All the strokes work together to produce one power stroke, and this power stroke drives the vehicle. In a four-stroke engine, the engine needs two crankshaft revolutions to produce power and drive the vehicle. So, various factors also affect the power generation of the engine.
Working Principle of Four-Stroke Engine
The four-stroke engine works in a continuous loop according to the Suction Stroke, Compression stroke, Power stroke, and Exhaust Stroke. These all stroke working are described below.
1. Suction Stroke
During the suction stroke, the piston is moved from T.D.C to B.D.C by the crankshaft, which is revolved either by the momentum of the flywheel or by the power generated by the electric starting motor. The inlet valve remains open and the exhaust valve is closed during the stroke. The downward movement of the piston sucks air and fuel mixture in the cylinder from the carburetor through the open inlet valve. In the diesel engine, only air was sucked into the cylinder. Here the crankshaft revolves around 1800.
2. Compression Stroke
During the compression stroke, the piston moves upward. The piston compresses the air-fuel mixture and the heat generated into the cylinder, makes a homogeneous mixture (14.7:1). The heat makes the petrol easier to burn while the compression forces it into closer combination with the air. The mixture under compression is ignited by the spark produced by a spark plug while the piston moves from B.D.C to T.D.C. Both the inlet and exhaust valve remain closed in this stroke. The crankshaft rotates at 1800
3. Power Stroke
The power stroke is known as a working or expansion stroke. The expansion of the gases due to the heat of combustion exerts pressure on the piston. Under this pressure, the piston then moves from T.D.C to B.D.C and
does the useful work. Both valves remain closed during the stroke. Here the crankshaft rotates 1800
4. Exhaust Stroke
During this stroke, the inlet valve remains closed and the exhaust valve opens. The greater part of the burnt gases escapes because of their expansion. The piston moves from B.D.C to T.D.C and pushes the remaining gases out of the exhaust valve. Only a small amount of exhaust gases remains in the clearance space which dilutes the fresh incoming charge. Here the piston rotates 1800.
Components of Four-Stroke Engine
A four-stroke engine works on several components like –
1. Valves
Engine valves are gates for the incoming air and fuel and the exit gate for the burnt gases. These valves are the most important components as they work together for efficient combustion in the engine.
2. Spark Plugs
Spark plugs are used basically in petrol engines. These spark plugs make an electrical spark on the fresh charge and burn it for efficient power inside the cylinder. These spark plugs are crucial for better engine running.
3. Piston
Pistons are used to compress the air-fuel mixture and also help to push out the burnt gas inside the cylinder. This piston is also used to act as a sealing media inside the cylinder.
4. Connecting Rod
Connecting rods are attached to the pistons and the crankshaft. This connecting rod makes a wide path and also helps absorb the thrust on the piston during the power stroke.
5. Crankshaft
Crankshafts act as a counter media and also act as a holding item of the whole operation. The moment of the crankshaft helps to generate the power inside the cylinder.
6. Cylinder
The cylinder is the space where the whole working of all strokes is placed. Inside the cylinder, the piston compresses the charge and according to that, all the members work.
Conclusion
Thus the four stoke was completed with the help of the piston and crankshaft. The crankshaft rotates a total of 7200 to complete all the strokes. Here The T.D.C means the top dead center into the cylinder, where the piston head appears. The B.D.C means the bottom dead center of the cylinder.