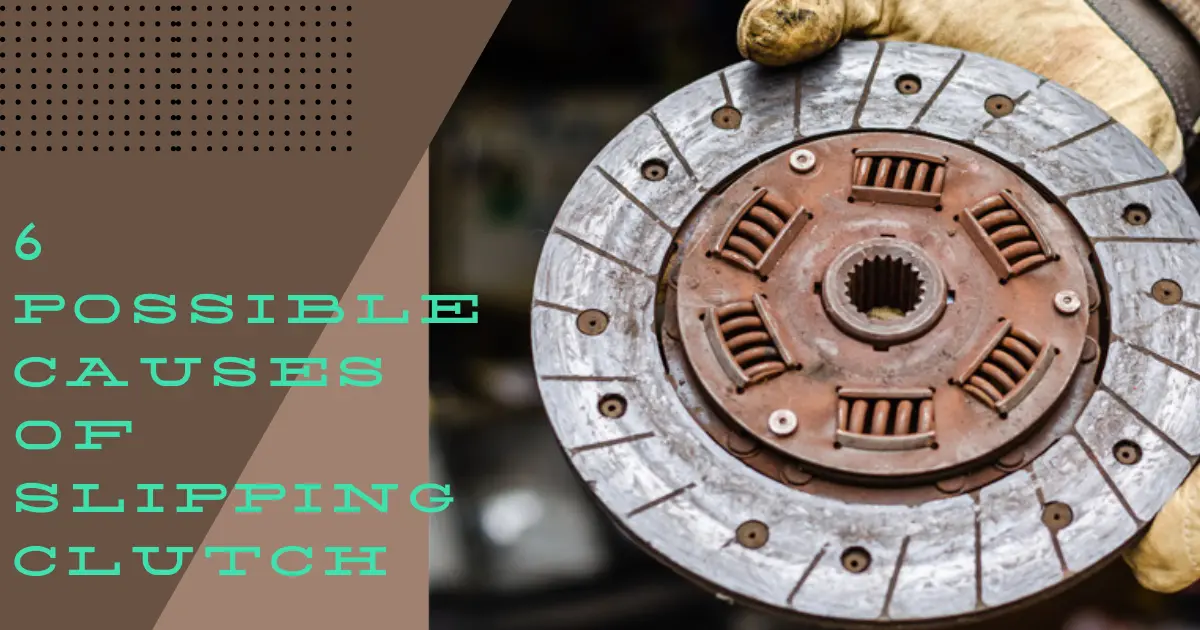
The clutch is an important component as it engages and disengages the engine power with the transmission system. This power cutoff is important as it helps to engage and disengage the transmission and varies the torque. In this article, I will discuss 6 possible causes of slipping clutch that you should know.
What is a Clutch?
A clutch is a mechanical device used in vehicles to engage and disengage power transmission between two rotating shafts. In a manual transmission car, the clutch is typically operated by the driver’s foot via a pedal. When the clutch pedal is pressed, the clutch disengages, allowing the engine to spin independently of the transmission.
Releasing the pedal engages the clutch, connecting the engine to the transmission, and enabling power to be transferred from the engine to the wheels. This allows the driver to change gears smoothly and control the vehicle’s speed.
Clutch has also components like pressure plate, springs, and clutch plate. All these members are working together to work with the engine. So, for synchronizing the gears with the engine this clutch is important for the safety of the transmission system.
6 Possible Causes of Slipping Clutch
Slipping the clutch means the clutch is not working properly, or when it is in an engaged position it misses the friction with the engine plate. In that case, the clutch will not be able to stop or resist the flow of power to the transmission.
So, for that, I will discuss 6 different types of possible causes of slipping clutch.
1. Loss of Clearance at the Tip of Release Fork
When there’s a loss of clearance at the tip of the release fork, it can lead to clutch slipping. The release fork is a component that’s responsible for disengaging the clutch when you press the clutch pedal. If there’s not enough clearance at the tip of the release fork, it may not fully disengage the clutch even when the pedal is pressed down.
This lack of full disengagement means that some power from the engine continues to transfer to the transmission, even when you’re not actively engaging the clutch. As a result, you might notice the engine revving up without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed, or the vehicle may struggle to accelerate smoothly. This phenomenon is known as clutch slipping, and it can lead to accelerated wear and tear on the clutch components, as well as decreased overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle.
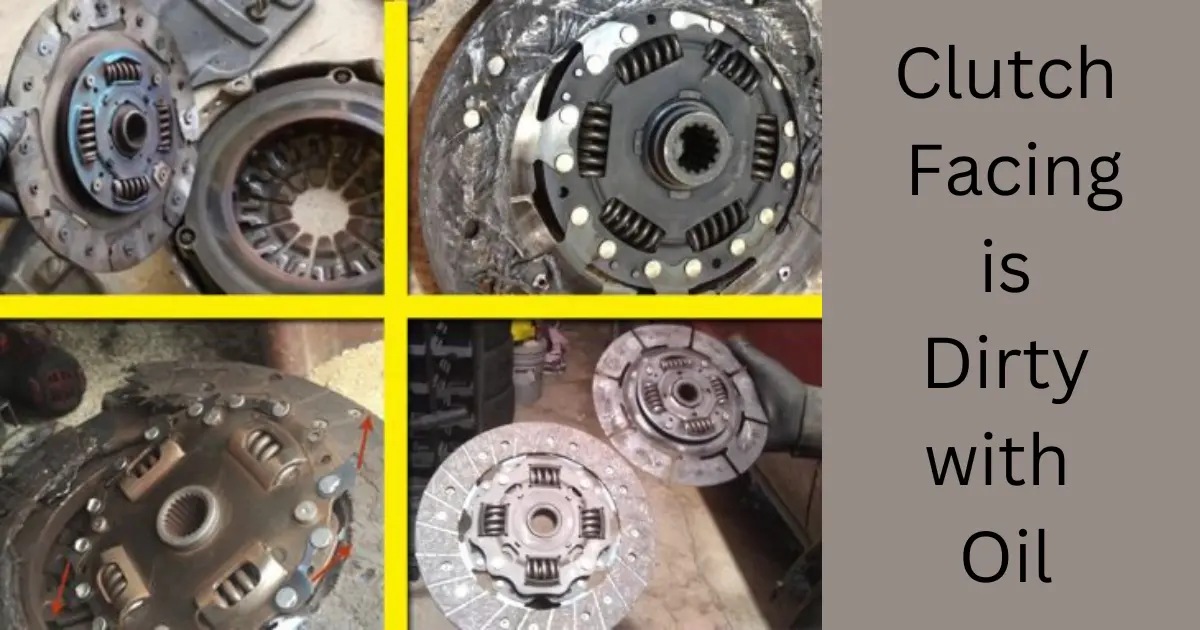
2. Clutch Facing is Dirty with Oil
When the clutch facing is dirty with oil, it can cause the clutch to slip. The clutch facing, also known as the clutch disc, is the component that engages with the flywheel to transmit power from the engine to the transmission.
If oil gets onto the clutch facing, perhaps due to a leak from the engine or transmission, it creates a slick surface. This oil contamination prevents the clutch facing from effectively gripping the flywheel, leading to a loss of friction and slipping. As a result, even when you engage the clutch fully, the transmission may not receive enough power from the engine, causing slippage.
3. Damaged or Worn Splines of Transmission Input Shaft
When the splines of the transmission input shaft are damaged or worn, it can lead to clutch slipping. The transmission input shaft is the component that connects the clutch to the transmission, allowing the engine’s power to be transmitted to the wheels.
If the splines on the input shaft are damaged or worn out, they may not engage properly with the corresponding splines on the clutch disc. As a result, the clutch disc may not be able to transmit power from the engine to the transmission efficiently, leading to slippage.
4. Weak Diaphragm Spring
When the diaphragm spring within the clutch assembly becomes weak, it can lead to clutch slipping. The diaphragm spring is a critical component responsible for applying pressure to the clutch disc, engaging it against the flywheel to transfer power from the engine to the transmission.
If the diaphragm spring loses its tension or becomes weakened over time, it may not exert enough force to fully engage the clutch disc against the flywheel. As a result, the clutch may slip, meaning that the power from the engine isn’t effectively transferred to the transmission.
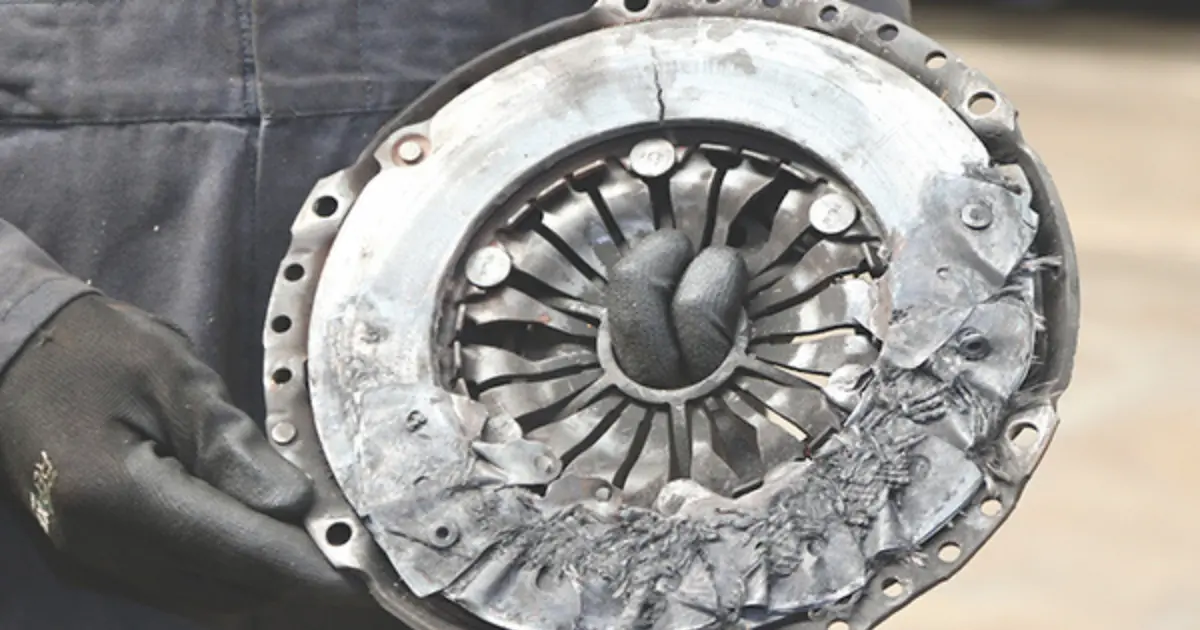
5. Distorted Pressure Plate or Flywheel Surface
When either the pressure plate or flywheel surface becomes distorted, it can cause clutch slipping. The pressure plate is a component that applies pressure to the clutch disc, while the flywheel is a rotating disk that stores rotational energy. Both play crucial roles in engaging and disengaging the clutch.
If either the pressure plate or flywheel surface becomes warped or distorted, they may not provide even pressure across the clutch disc. This uneven pressure can result in the clutch disc not fully engaging against the flywheel, leading to slipping.
6. Not Enough Play of Clutch Pedal
When there’s not enough play in the clutch pedal, it can lead to clutch slipping. The play in the clutch pedal refers to the amount of free movement or clearance before the clutch begins to engage.
If there’s insufficient play in the clutch pedal, it means that the clutch may not be fully disengaging even when the pedal is pressed. As a result, the clutch disc remains partially engaged with the flywheel, causing slipping.
If you addressing such issues this is adviseable to visit your nearest showroom to change or repair the parts. The clutch is important for the safety of the engine also. So, a single change can cost you a lot.
Conclusion
So, the clutch is the main important component that connects and disconnects the engine power to the transmission. For better operation of the clutch, the vehicle should follow the guidelines to maintain it properly. Please visit the nearest showroom for better and smoother performance of the clutch.
Read More- Do EV Cars have Transmissions?